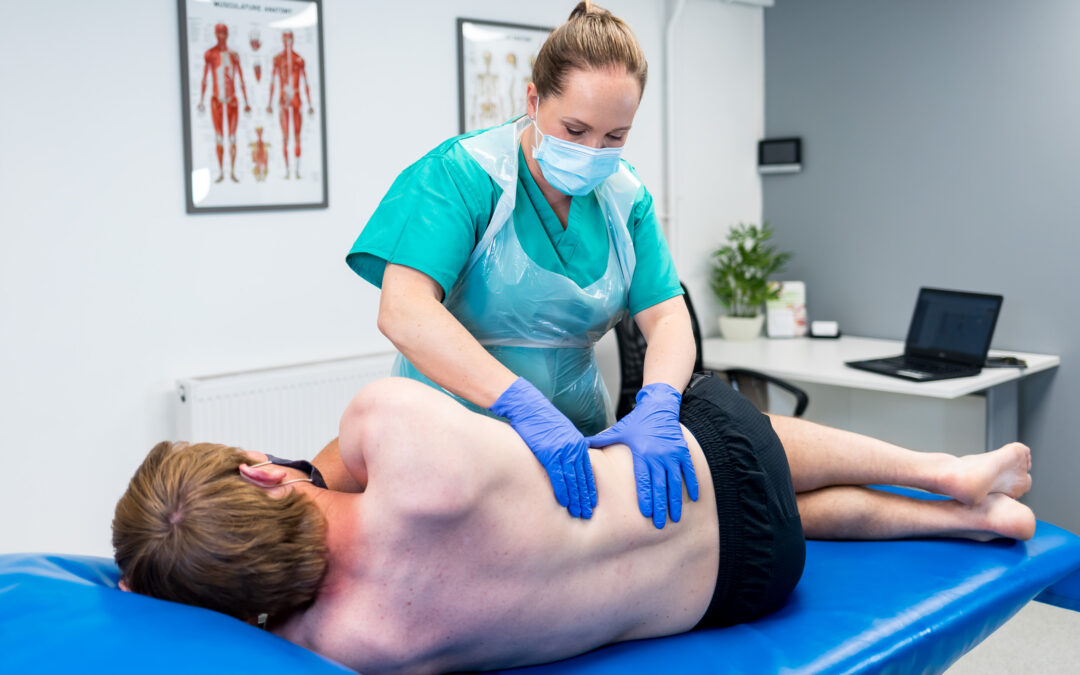
Osteopathy is a complementary or alternative medicine (CAM) when used outside of the US. It is founded on the principle that our general wellbeing depends upon our ligaments, muscles, joints and connective tissue working together. Osteopaths aims to find, prevent and heal sources of pain by massaging and manipulating the client’s muscles and joints.
When is Osteopathy used?
Osteopathy is often used on patients who suffer from lower back pain, sports injuries, arthritis, shoulder and neck pain. However, some osteopaths have promoted the use of such treatment on period pains and migraines but the evidence for its success is limited. Additionally, Osteopaths are qualified to identify problems for which a client may need to seek further medical investigation in the form of blood tests or MRI scans.
Osteopathy sessions often last just under an hour in which the practitioner will first address the client’s general health before physically examining the client’s symptoms. The client may have to remove clothing so that the practitioner can address the affected areas. They use their hands to massage, stretch stiff joints and to move the body in its natural way (known as articulation). They may also use high-velocity thrusts in a motion with sharp movements to the spine. Practitioners must be registered with the General Osteopathic Council (GOsC) in order to call themselves osteopaths and use this method on clients.